Natural logarithm
log(eⁿ ) = n
log(e⁰ ) = 0 = log(1)
log(e¹ ) = 1 = log(e)
log(e² ) = 2
log(e⁻¹) = -1 = log(1/e)
log(x * y) = log(x) + log(y)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0.01, np.e**2 + 0.1, 100)
y = np.log(x)
plt.plot(x, y, label='log(x)')
def mark_coord(x, label, offset):
y = np.log(x)
plt.scatter(x, y, color='red')
plt.annotate(label, (x, y), textcoords="offset points", xytext=offset , ha='center', fontsize=8, color='red')
mark_coord( 1/np.e , 'log(1/e)', ( 22, -7))
mark_coord( 1 , 'log(1)' , ( 14,-10))
mark_coord( np.e , 'log(e)' , (-10, 6))
mark_coord( np.e**2 , 'log(e^2)', (-10,-11))
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('log(x)')
plt.title('Natuaral logarithm')
plt.grid()
plt.savefig('img/natural-logarithm.png')
Logistic function
The logistic function is a
sigmoid function and thus
- produces a value between 0 and 1
- is defined for all real input values
- has a non-negative derivatative at each point
- exactly one inflection point (which IMHO makes the derivative bell shaped?)
The inverse of the logistic function is the logit function.
The following plot draws the
standard logistic function:
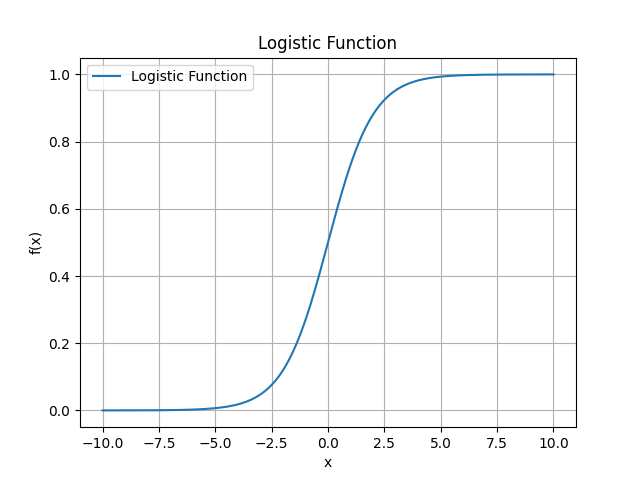
It was created with
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def standard_logistic(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
x_values = np.linspace(-10, 10, 400)
y_values = standard_logistic(x_values)
plt.plot(x_values, y_values, label='Logistic Function')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('f(x)')
plt.title("Logistic Function")
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
# plt.show()
plt.savefig('img/standard-logistic-function.png')
TODO
Sigmoid functions are commonly used as activation funcions in neural networks.
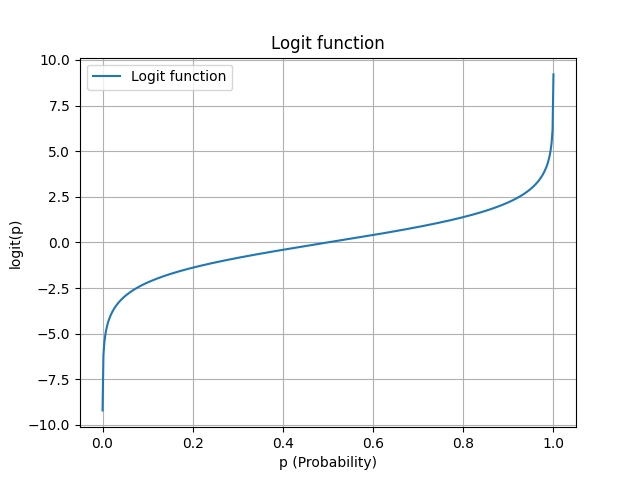
Logit function
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def logit(p):
return np.log(p / (1 - p))
p_values = np.linspace(0.0001, 0.9999, 500)
y_values = logit(p_values)
plt.plot(p_values, y_values, label='Logit function')
plt.xlabel('p (Probability)')
plt.ylabel('logit(p)')
plt.title('Logit function')
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
# plt.show()
plt.savefig('img/logit.png')
softmax
softmax takes k numbers and produces k numbers each of which is between 0 and 1 and whose sum is equal to 1.
The softmax function is often applied as final function to a neural network.
The following Python script computes the softmax of the values stored in z:
import math
z = [ 0.8, -0.2, 2.1, 1.3, -0.8]
# temporary values:
t = [ math.e ** z_ for z_ in z ]
σ = [ t_ / sum(t) for t_ in t ]
for i , σ_i in enumerate(σ):
print(f'σ_{i} = {σ_i:04.3f}')
print(f'Sum(σ) = {sum(σ):04.3f}')
When executed, the script prints:
σ_0 = 0.145
σ_1 = 0.053
σ_2 = 0.533
σ_3 = 0.239
σ_4 = 0.029
Sum(σ) = 1.000